Synthetic vs Natural Fiber Ribbon Cutting: The Chemistry of the Cut

In the world of industrial cutting, "Material dictates Method." I often receive samples from clients asking why their machine is burning their tape or why the edge is fraying. The answer almost always lies in the chemistry of the fiber.
The primary difference between Synthetic and Natural fiber ribbon cutting is the reaction to heat. Synthetic fibers (Nylon, Polyester) are thermoplastics that melt, requiring Hot Cutting to seal the edge. Natural fibers (Cotton, Jute) are cellulose-based and burn, requiring Cold Cutting to prevent charring. Choosing the wrong method results in damaged product or fire hazards.
At HAOXINHE, we build machines for everything from delicate silk to heavy-duty parachuting ropes. Understanding this distinction is the first step to selecting your webbing tape cutting machine1.
The Chemistry: Why Heat Works (Or Doesn’t)
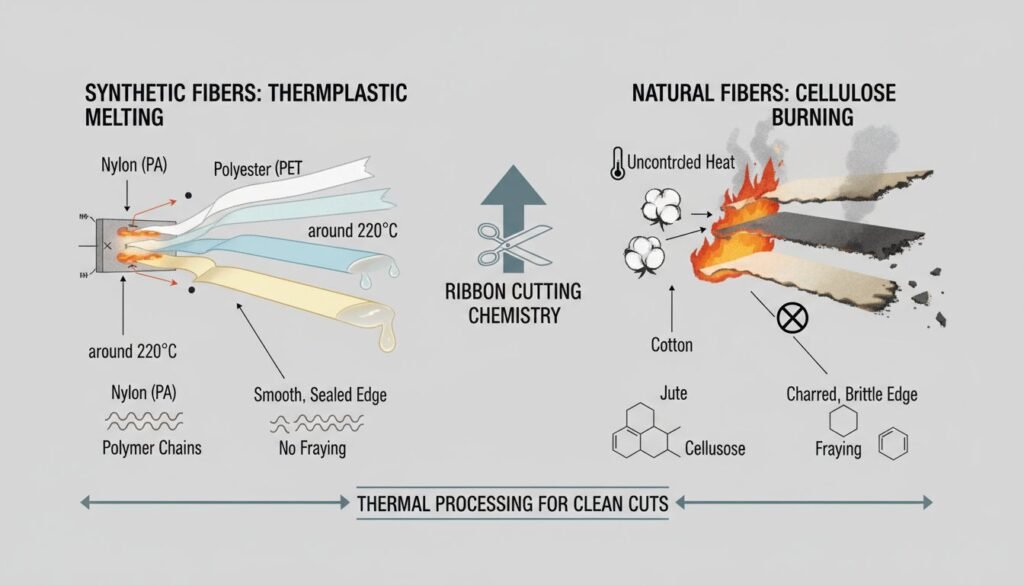
1. Synthetic Fibers (Thermoplastics)
- Examples: Polyester (PET), Nylon (Polyamide), Polypropylene (PP), Acrylic.
- Behavior: These are essentially oil-based plastics spun into threads. When heated to their specific melting point (e.g., Nylon at ~220°C), they turn into a liquid. When cooled, they form a solid solid plastic bead.
- Cutting Goal: Controlled Melting. We want to fuse the warp and weft threads together to stop fraying.
2. Natural Fibers (Cellulose/Protein)
- Examples: Cotton, Jute, Hemp, Silk, Wool.
- Behavior: These are organic. They do not have a melting point; they have an ignition point. If you apply a hot knife to cotton, it acts like paper—it smokes and turns to black ash.
- Cutting Goal: Clean Separation. We want a sharp shear cut. Sealing is impossible with heat; it must be done by sewing or gluing later.
Deep Dive: Matching Machine to Material
Here is how we categorize machines at HAOXINHE based on material groups.
Group A: The Synthetics (Hot Cutting2)
For most modern webbing, heat is mandatory.
- Light Duty: Satin, Grosgrain. Standard Hot Knife.
- Heavy Duty: Climbing Ropes, Safety Harnesses.
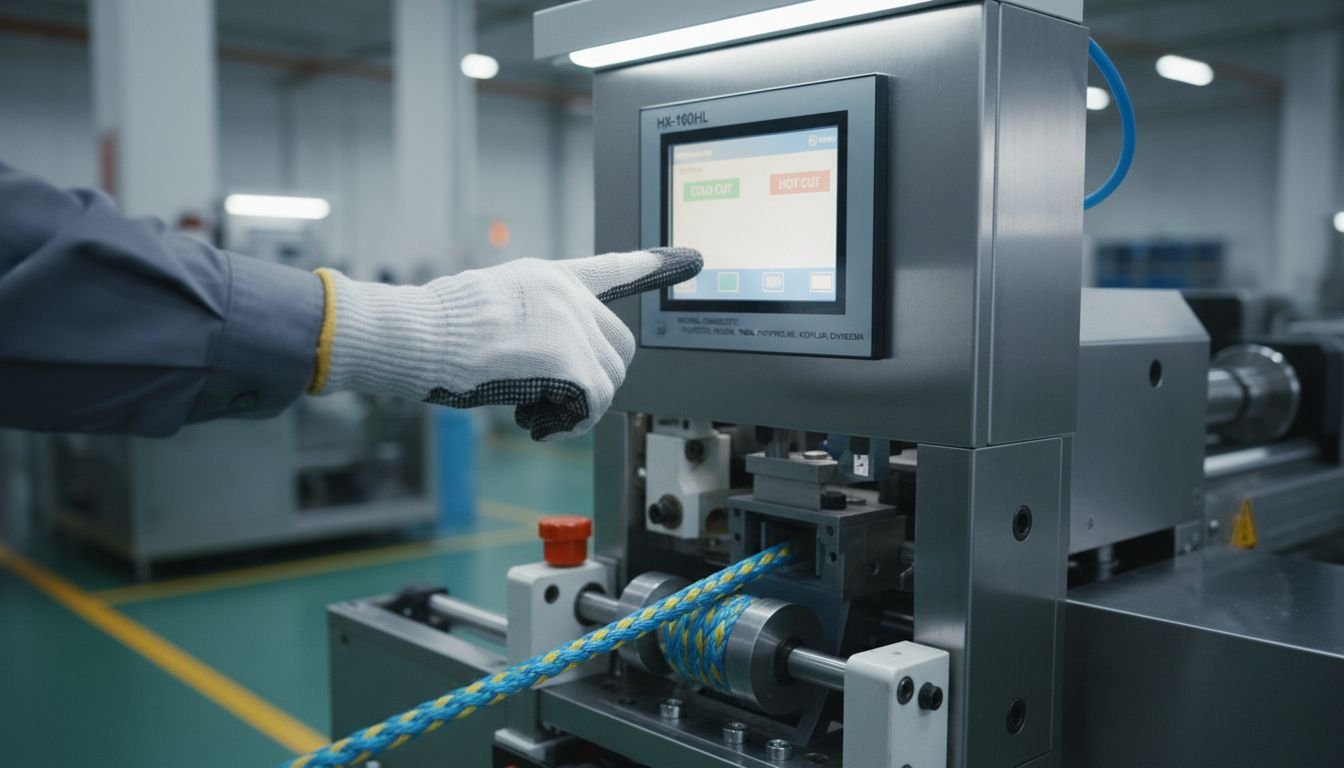
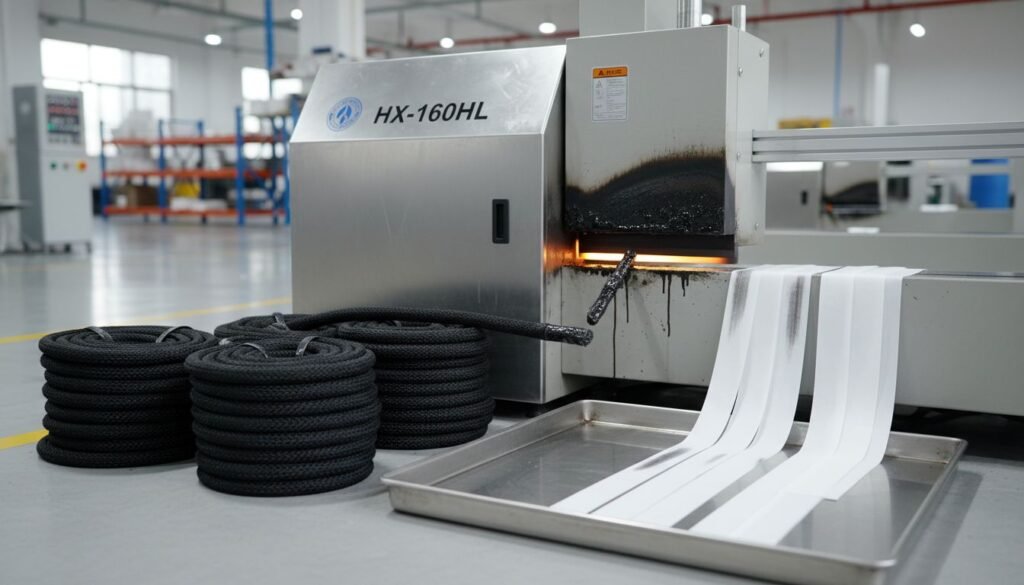
This is where our HX-160HL Parachuting Climbing Webbing Rope Cutting Machine3 shines. Climbing ropes are made of high-tenacity Nylon 66. They are thick and round. A standard hot knife cannot penetrate them efficiently. The HX-160HL uses a high-power thermal blade specifically designed to slice through thick bundles of synthetic fibers and seal the core instantly to prevent "blooming."
👉: [HX-160HL Parachuting Climbing Webbing Rope Cutting Machine](https://www.hexinmachines.com/HX-160-Automatic-Roll-To-Sheet-Wire-Cable-Rubber-Tube-Cutting-Machine-pd40519883.html)3
Group B: The Naturals (Cold Cutting)
For eco-friendly or traditional materials, you need sharpness.
- Machines: Computer tube cutting machine (Cold blade version), Guillotine cutters.
- Challenge: Because the edge is raw, it will fray.
- Solution: Many factories use our cold cutters to cut to length, then immediately pass the piece to an automated sewing machine to fold and hem the edge.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Synthetic (Nylon/Poly) | Natural (Cotton/Jute) |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction to Heat | Melts / Fuses | Burns / Chars |
| Best Cutting Method | Hot Knife / Ultrasonic | Cold Blade / Guillotine |
| Edge Result | Sealed / Hard | Raw / Soft |
| Machine Example | HX-160HL Parachuting Cutter | HX-980 Cold Cutter |
| Post-Processing | None | Sewing / Gluing Required |
Industrial / Manufacturing Considerations

If you are a contract manufacturer, you likely handle both.
The Risk of Cross-Contamination
If you cut black nylon on a hot machine, residue builds up on the blade. If you then try to cut white polyester, that black residue will transfer, ruining the batch.
- Cherry’s Tip: We recommend dedicated machines for different color families, or rigorous blade cleaning protocols.
Safety Factors
- Synthetics: Fumes are plastic smoke (toxic over time). Ventilation is key.
- Naturals: Dust and lint. Cotton cutting creates fine dust that is a fire hazard. Your machine needs to be blown out with compressed air daily.
Heavy Industry Focus
For sectors like Automotive & HVAC, you might use materials that are composites (e.g., fiberglass mixed with plastic). These require testing. We often use our metal pipe cutting and beveling machine4 technology to adapt cutters for these super-tough industrial materials.
How Machines Solve This Problem
At HAOXINHE, we don’t guess. We rely on the specs.
For the toughest synthetic jobs—like Parachuting and Climbing Ropes—we built the HX-160HL.
- Why it’s special: It doesn’t just get hot; it maintains thermal mass. When a cold rope touches a hot blade, it sucks the heat away. The HX-160HL has enough power to keep the blade at 300°C even while cutting 20mm ropes continuously. This ensures every rope end is safe, sealed, and life-saving grade.
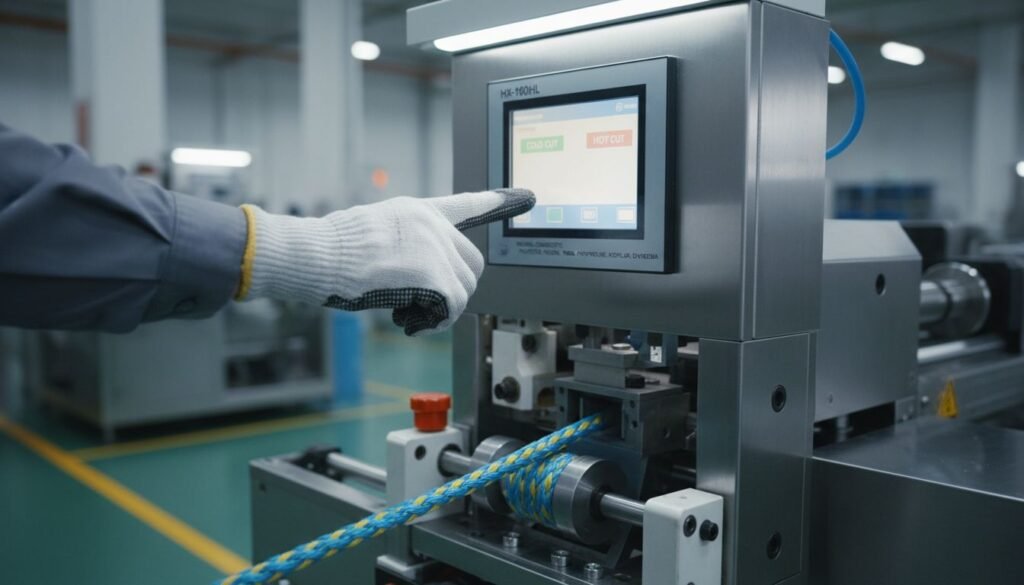
For mixed factories, our hot and cold cutting machine allows you to toggle the heating element. It gives you the flexibility to say "Yes" to both the Cotton Tote Bag order and the Nylon Cargo Strap order.
Conclusion

To summarize, chemistry dictates the cut. Do not try to hot-cut cotton, and do not try to cold-cut nylon (unless you want to sew it). For critical safety applications involving heavy synthetics, trust specialized equipment like the HX-160HL.
Cherry’s Insights for Google Snippet
Synthetic fibers (Nylon, Polyester) are thermoplastics that must be cut with a Hot Knife to melt and seal the edges, preventing fraying. Natural fibers (Cotton, Jute) are cellulose-based and will burn if heated; they require Cold Cutting (mechanical shearing) followed by sewing or gluing. For heavy-duty synthetics like climbing ropes, use high-power thermal cutters like the HAOXINHE HX-160HL to ensure a safe, deep seal.
-
Find out how webbing tape cutting machines enhance efficiency in fabric cutting. ↩
-
Discover the hot cutting process and its importance in working with synthetic materials. ↩
-
Explore the advanced features of the HX-160HL for cutting tough synthetic materials. ↩ ↩
-
Find out how metal pipe cutting and beveling machines are utilized in industrial applications. ↩


